About IJDDC. International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries is the official peer-reviewed journal of Research Society for the Study of Diabetes in India (RSSDI)commanding a membership of over 10,500+ at present being hosted online by publishers Springer Nature. The primary goal of the journal is to serve as an important, all.. Once considered a disease of affluent countries, nearly 80% of people with diabetes, mainly type 2, now live in low- and middle-income countries [].Furthermore, its prevalence is rapidly rising, with the largest increases foreseen in Africa, the Middle East, South East Asia and Central America [].Worldwide, the increase in the proportion of people over 65 years old is a major factor driving.

British Journal of Diabetes

Dr. Rodica PopBusui Publishes STRIDE protocol in Journal of Diabetes and its Complications

(PDF) World Journal of Diabetes

Diabetes Journal, Volume 64, Issue 7, July 2015

(PDF) International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries Nima Rezaei Academia.edu

(PDF) Diabetes prevalence and its risk factors in urban Puducherry

Diabetes in developing countries Misra 2019 Journal of Diabetes Wiley Online Library

(PDF) Depression and type 2 diabetes in developed and developing countries

Global distribution of diabetes prevalence in 2017 Download Scientific Diagram

International Journal of Diabetes Template Scitech Central

Diabetes in developing countries Misra 2019 Journal of Diabetes Wiley Online Library

(PDF) Challenges to diabetes selfmangement in developing countries

(PDF) Value of mobile monitoring for diabetes in developing countries
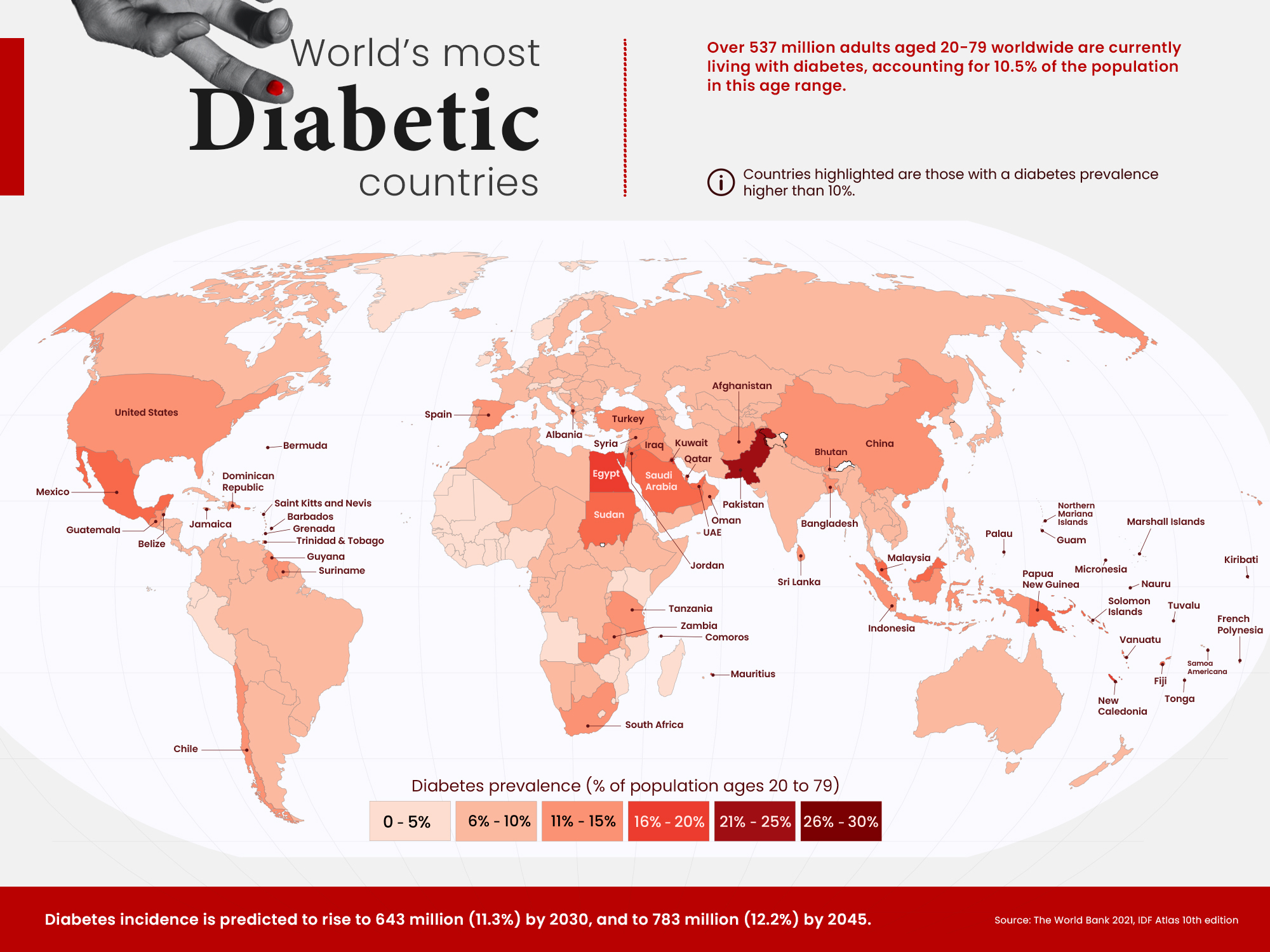
World's Most Diabetic Countries

International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries Incorporating Diabetes Bulletin

Diabetes Research Journal of Diabetes Open Access

(PDF) 0123456789) 1 3 International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries

(PDF) The economic costs of diabetes in developing countries Some concerns and

(PDF) Primary prevention of type2 diabetes in developing countries

(PDF) Diabetes in Developing countries
Abstract. en. There has been a rapid escalation of type 2 diabetes (T2D) in developing countries, with varied prevalence according to rural vs urban habitat and degree of urbanization. Some ethnic groups (eg, South Asians, other Asians, and Africans), develop diabetes a decade earlier and at a lower body mass index than Whites, have prominent.. With the growing prevalence of type 2 diabetes, particularly in emerging countries, its management in the context of available resources should be considered.. Management of Type 2 Diabetes in Developing Countries: Balancing Optimal Glycaemic Control and Outcomes with Affordability and Accessibility to Treatment Diabetes Ther. 2020 Jan;11(1.