How emulsions and emulsifiers work. Simple emulsions are either oil suspended in an aqueous phase (o/w), or water suspended in oil (w/o). Milk is an example of an o/w emulsion, in which the fat phase or cream forms tiny droplets within the skim milk, or water phase. In contrast, margarine is a w/o emulsion containing droplets of water or skim.. In this work, we investigate droplet coalescence in flowing oil-in-water emulsions subjected to higher than room temperatures namely between 20 to 70 \ (^ {\circ }\) C. We use a specifically.

Multiple WaterinOilinWater Emulsion Gels Based on SelfAssembled Saponin Fibrillar Network
Processes Free FullText The Formation, Stabilization and Separation of OilWater Emulsions
Emulsions Definition, Preparation, Working, Types, Properties, Application, and Harmful Effects
16. What is the difference between oil in water emulsion and water in oil emulsion
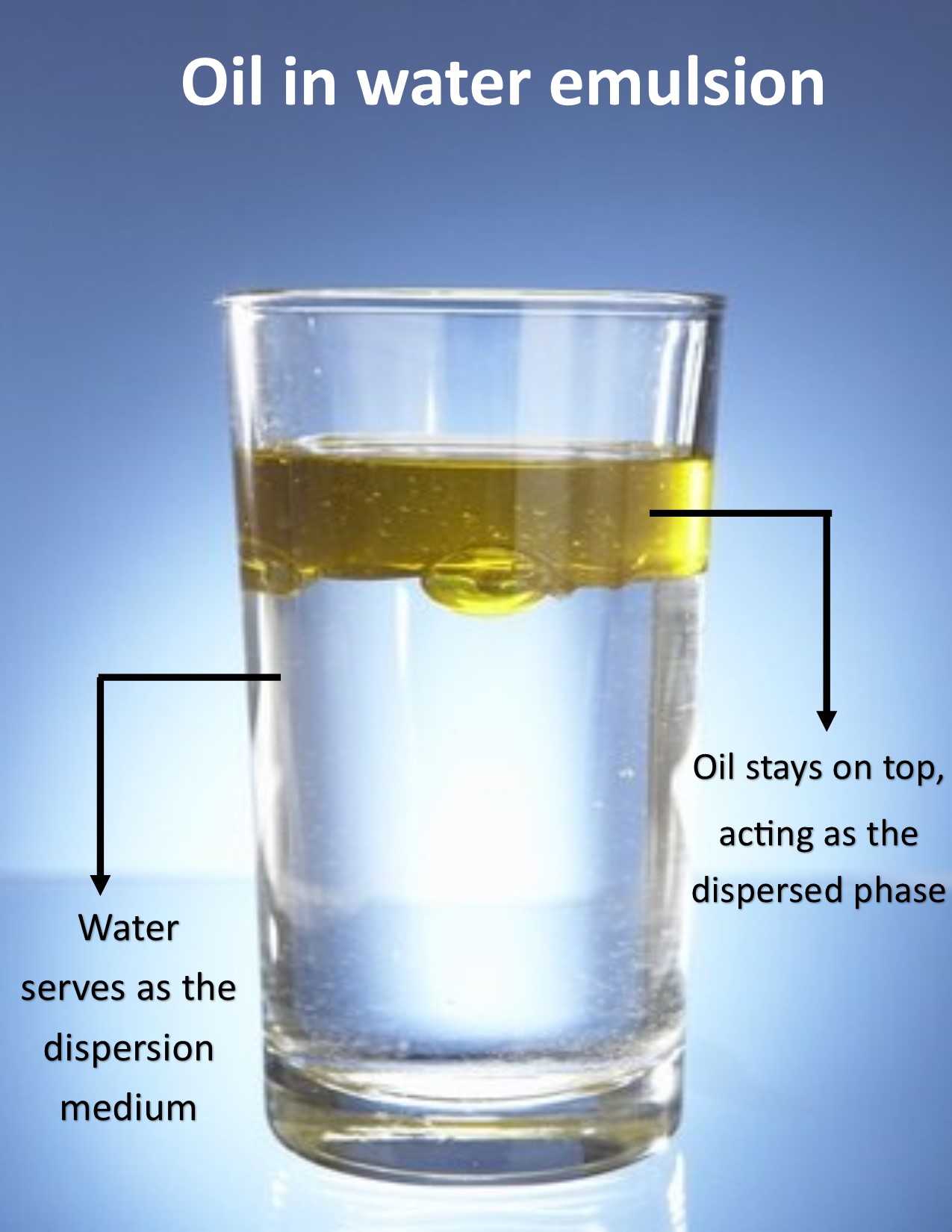
Emulsion definition, properties, and examples The Science Core

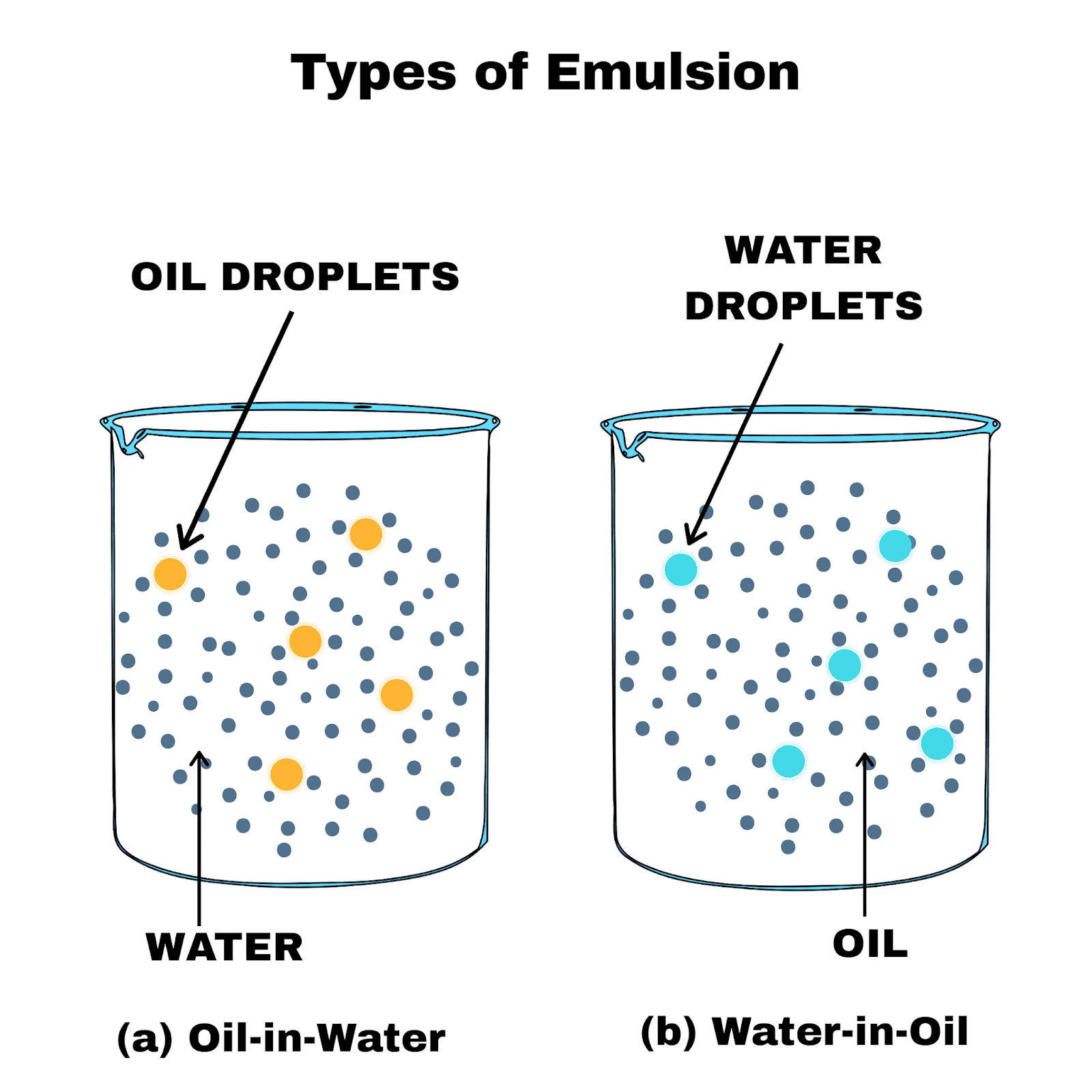
how can the emulsion of oil in water and water in oil be distinguished Chemistry Surface

Schematic of nanoemulsion systems oil in water (O/W) and water in oil... Download Scientific

Emulsion. Experiment with Oil and Water Stock Vector Illustration of chemistry, unmixable

Water in Oil Emulsion Definition, Example, and Solution Ginhong
An illustration of immiscible liquids water and oil in an emulsion Stock Photo Alamy
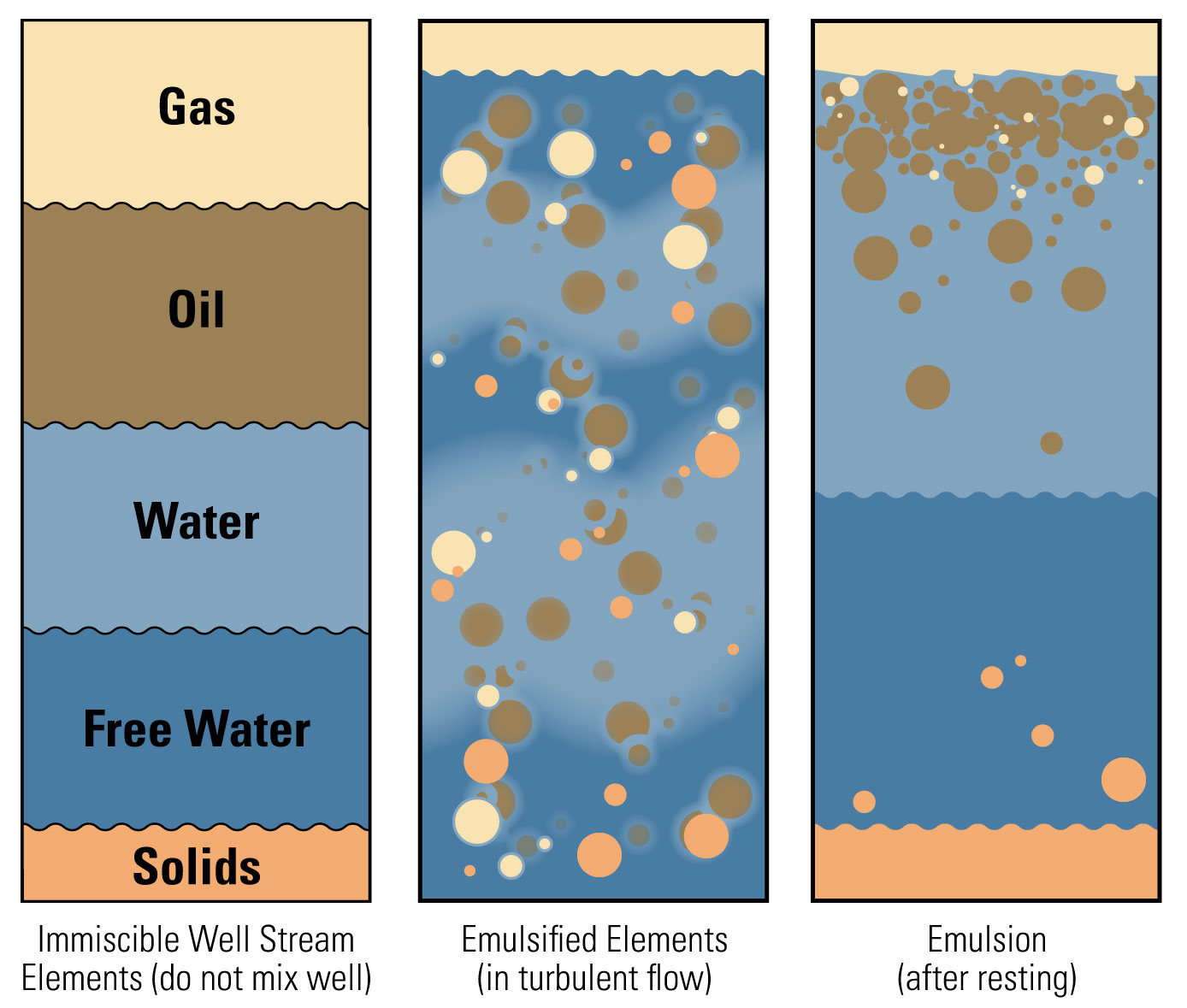
What is an Oil Emulsion? Kimray

Oil in Water vs Water in Oil Emulsions Fast differences and Comparison YouTube

Making a Water in Oil Emulsion with Lecithin YouTube

8 Formation of waterinoil emulsion (Modified from Lee, 1999) Download Scientific Diagram

Emulsifier Defination, Classification, Properties & Uses
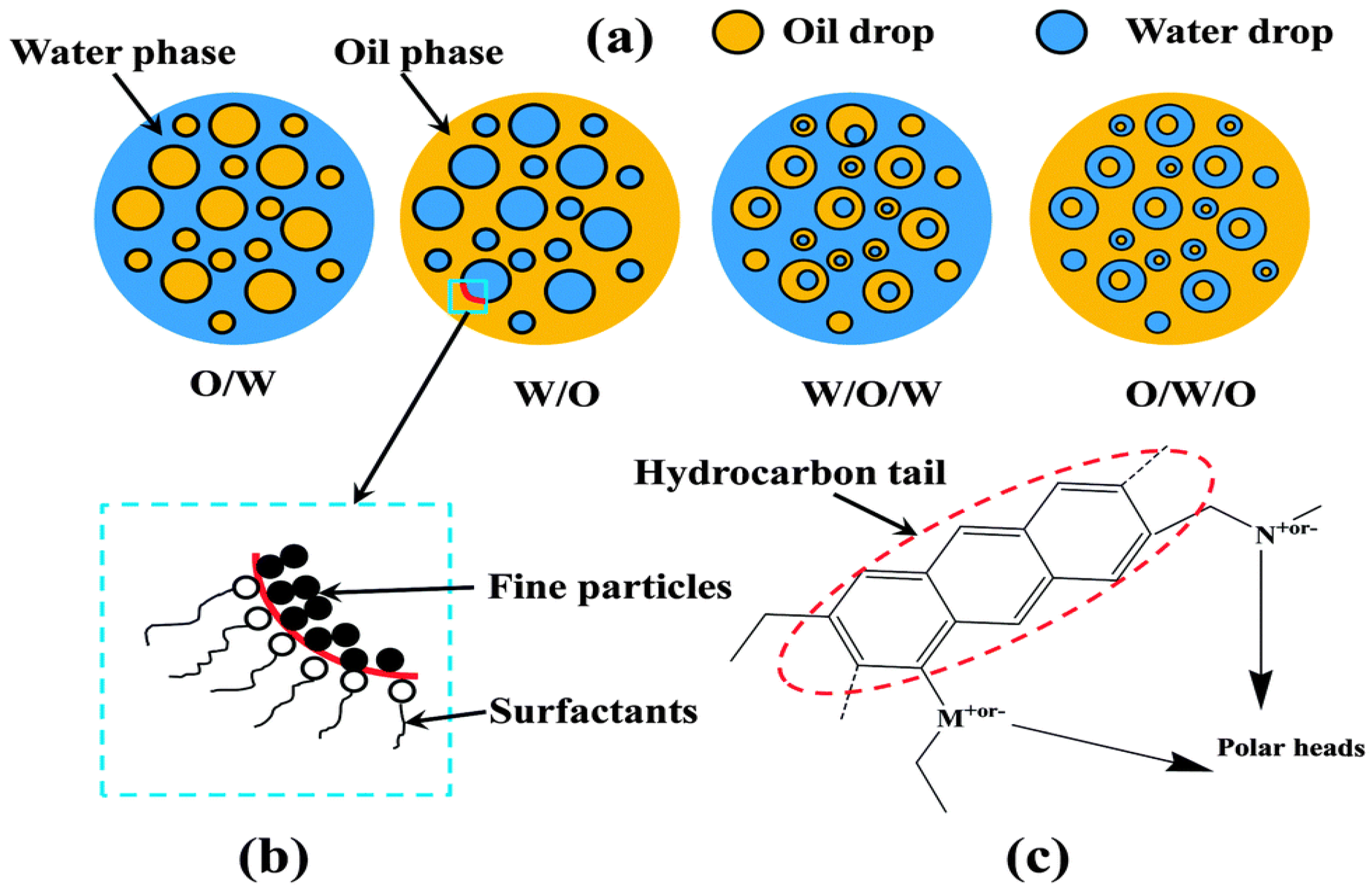
Processes Free FullText The Formation, Stabilization and Separation of OilWater Emulsions

ABE researchers develop new way to mix oil and water News College of Engineering Purdue

(a) Oilinwater and waterinoil emulsion stabilized by responsive... Download Scientific Diagram

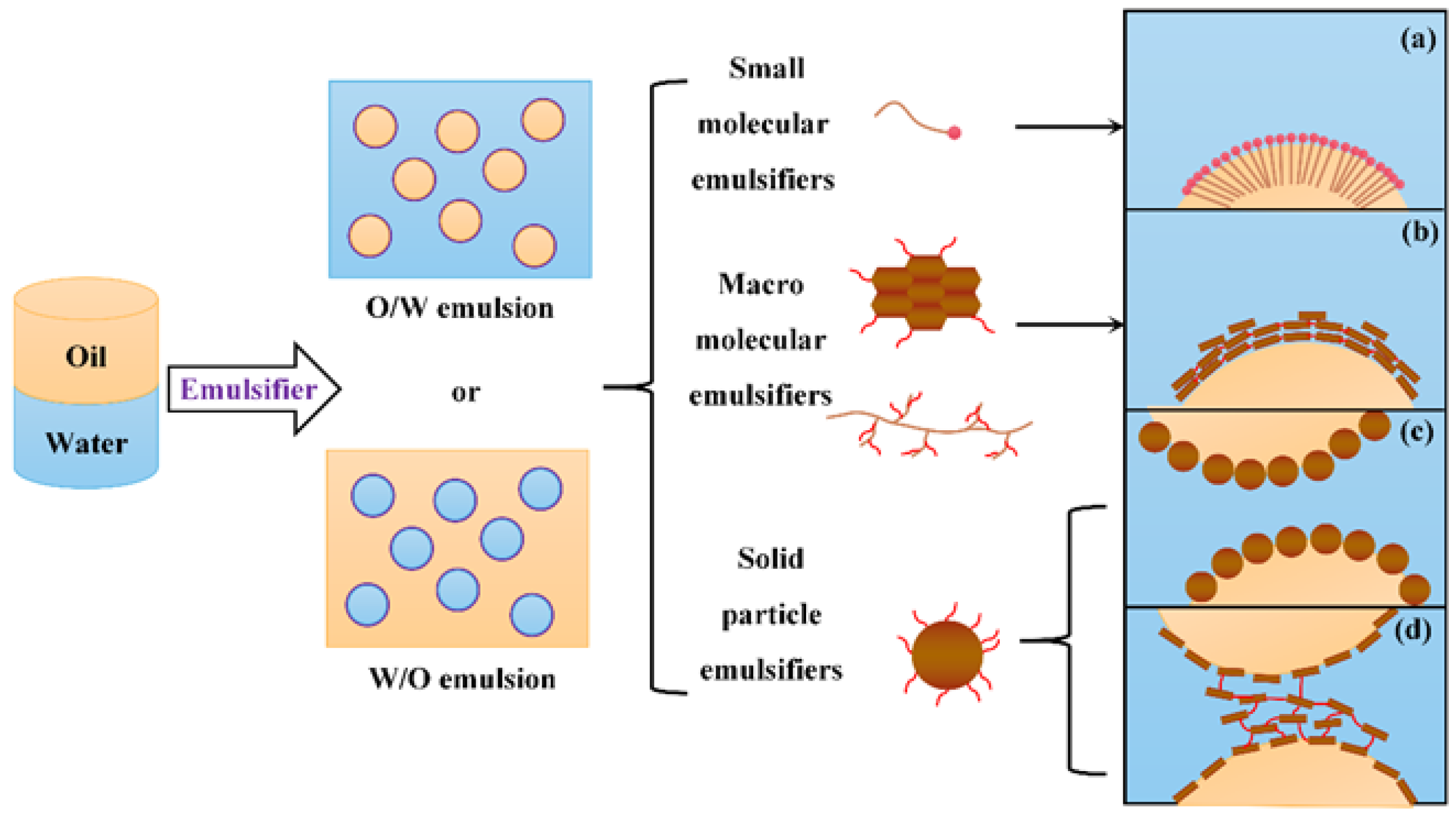
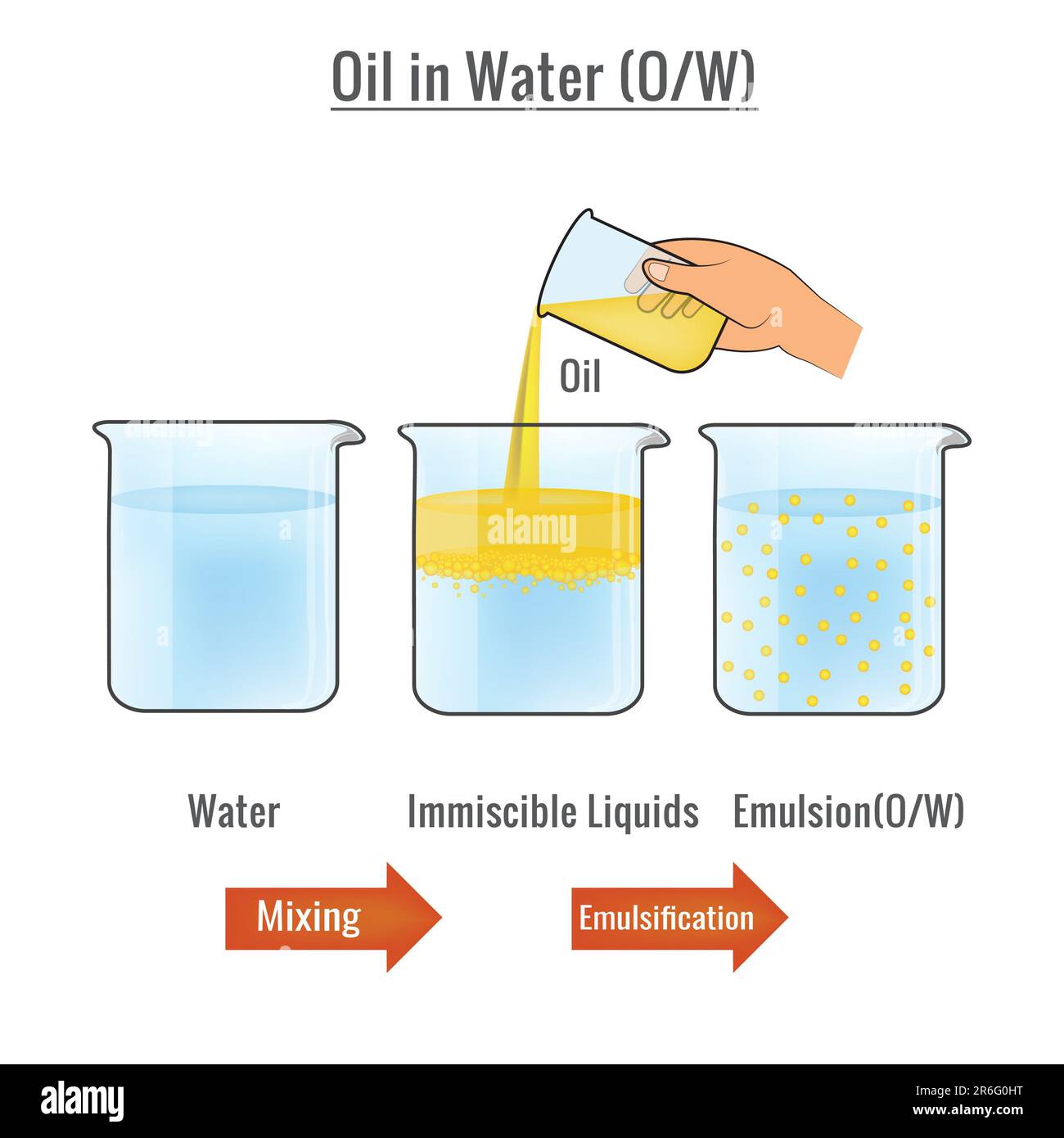
Emulsion formation from oil and water by addition of an emulsifier Download Scientific Diagram
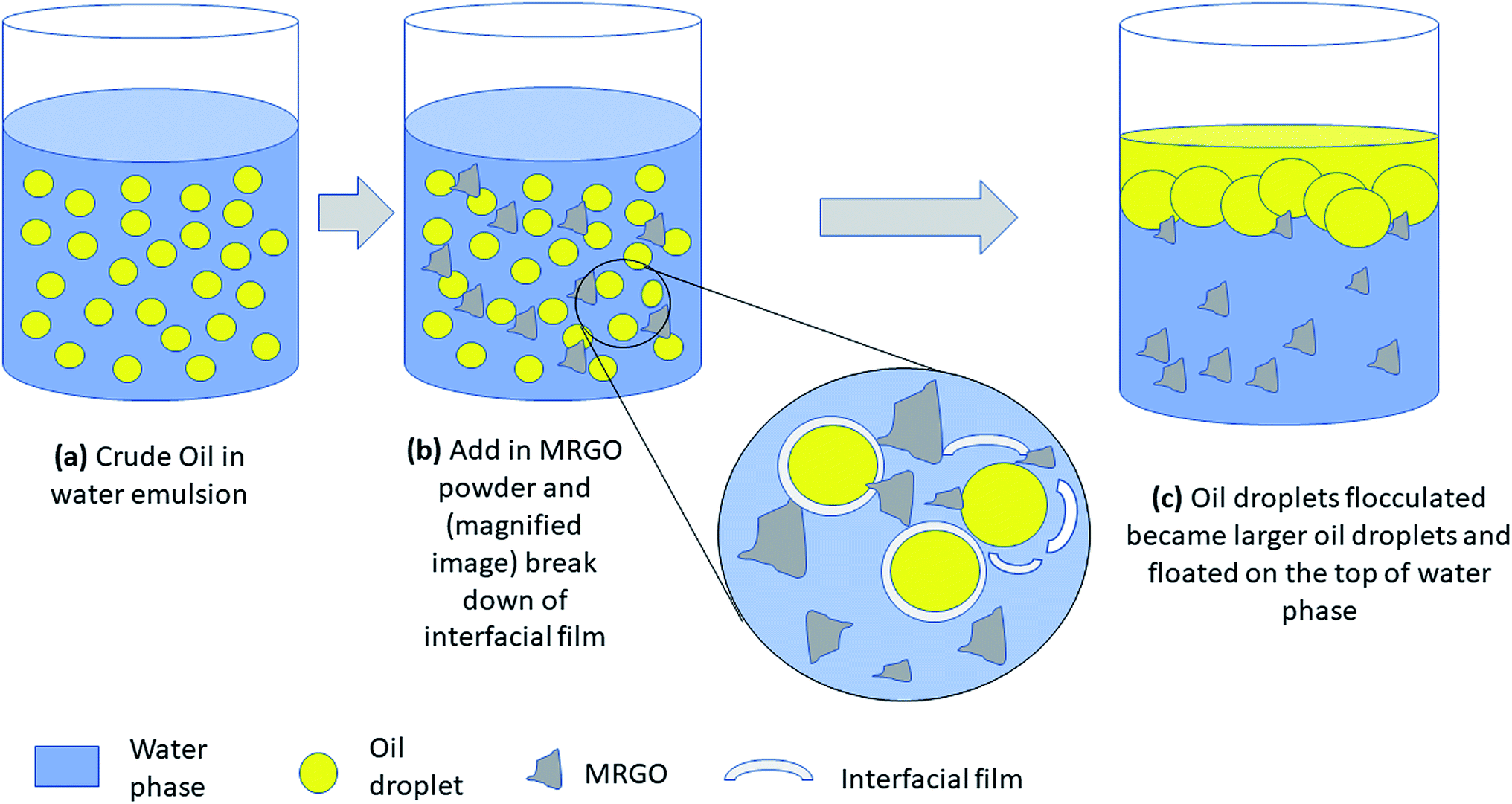
Optimization and characterization of graphene oxide for
Designing water-in-oil (W/O) emulsions is a promising strategy to incorporate water. • W/O emulsions stabilized by surfactants, biopolymers and/or particles are reviewed. • There is a growing need for emulsifiers that are 'clean-label' and biodegradable. • Use of bio-derived Pickering particles is a relatively recent endeavour.. A review of numerical modelling schemes for the formation of water-in-oil emulsions is given. A recent model is based on empirical data and the corresponding physical knowledge of emulsion formation.